Cash Back Mortgages – 6 Things You Need to Know

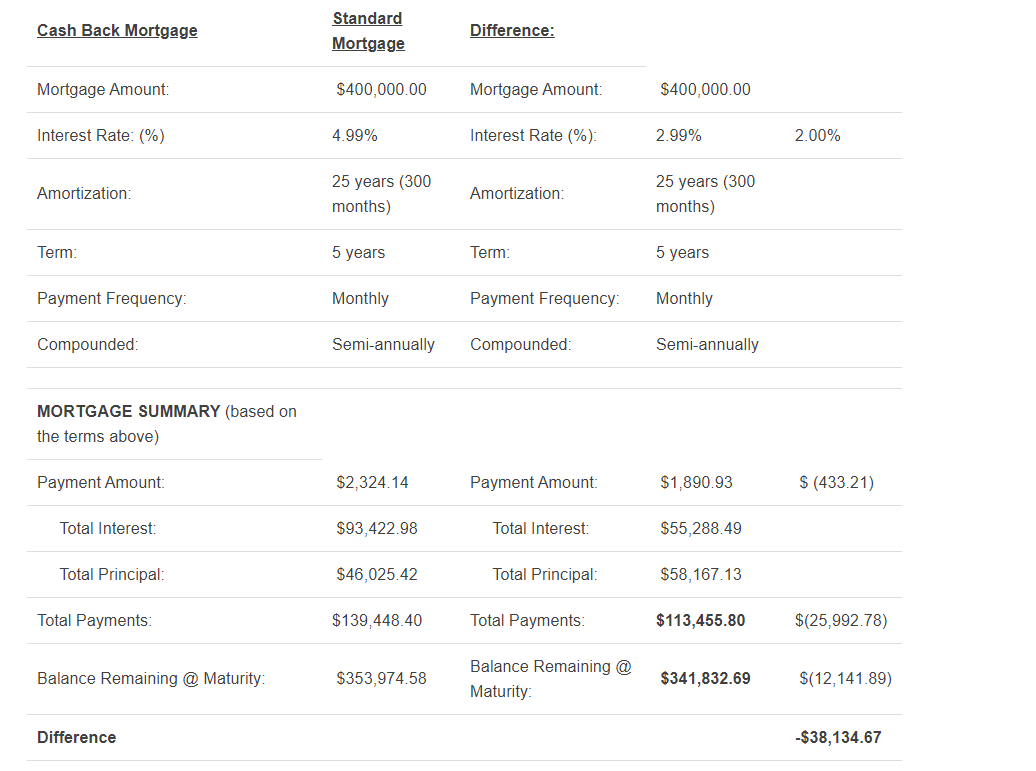
$38,000 difference over 5 years. It’s pretty clear why a Cash Back Mortgage may not be a great deal for the home buyer.
2) Cash back mortgages are only available on fixed-term mortgages of five years. The mortgage must be insured or insurable so that means the property value can’t be any higher than $999,999.
3) Claw back penalties: If you need to break your mortgage early, whether to sell or refinance your home before your 5-year mortgage term is complete.… you have to pay the Penalty PLUS return the Cash Back portion to the bank. The Cash Back Penalty is sometimes prorated OR sometimes you need to pay the full amount back, depending on the lender. Check the fine print of your mortgage contract.
4) Variable rate mortgages are not available for Cash Back.
5) Limited availability:
Most lenders offering Cash Back Mortgages are looking for A+ borrowers with a solid credit profile, steady provable income, and typically 5% or more down payment.
6) Cash Back mortgages are available for purchases and mortgage transfers of owner-occupied homes only and not second homes or rental properties.
READ the FINE PRINT. Many people are so excited about the cash back (FREE money who wouldn’t be excited!!!), they miss the fine print on lender’s websites and in their mortgage contract. When a deal seems to be too good to be true, there is always a catch… There is NO Free lunch!
Cash Back mortgages are not offered by all lenders. As a mortgage broker, I have several lenders that offer various types of cash back mortgages. We will review your personal situation, crunch the numbers to ensure that you are fully aware of all the pros and cons of committing to a Cash Back mortgage.
If you are interested in learning more about a Cash Back mortgage or if you currently have a Cash Back mortgage and have questions, let’s have a chat.
Buying a home is both: exciting and nerve wracking. My job is to simplify and educate you about mortgages, so you make good decisions based on your situation.
Kelly Hudson
Mortgage Expert
Mobile: 604-312-5009
Kelly@KellyHudsonMortgages.com
www.KellyHudsonMortgages.com



Let's do this together.
Sign up to our newsletter
Thank you for contacting me.
I will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later
All Rights Reserved | Mortgage Architects