Everything You Need to Know about Mortgage Default Insurance. (updated June 2025)
Home buyers say the #1 obstacle to homeownership is saving enough money for a down payment.
Mortgage default insurance (also called mortgage insurance) allows you to purchase a home with as little as
5% down. It protects your lender if you stop making payments.
Typically, a 20% or higher down payment is your best option. However, for many Canadians, reaching this amount can be challenging, especially in expensive markets like Greater Vancouver & Toronto.
If you don't have enough cash for a 20% down payment, Mortgage Default Insurance can help.
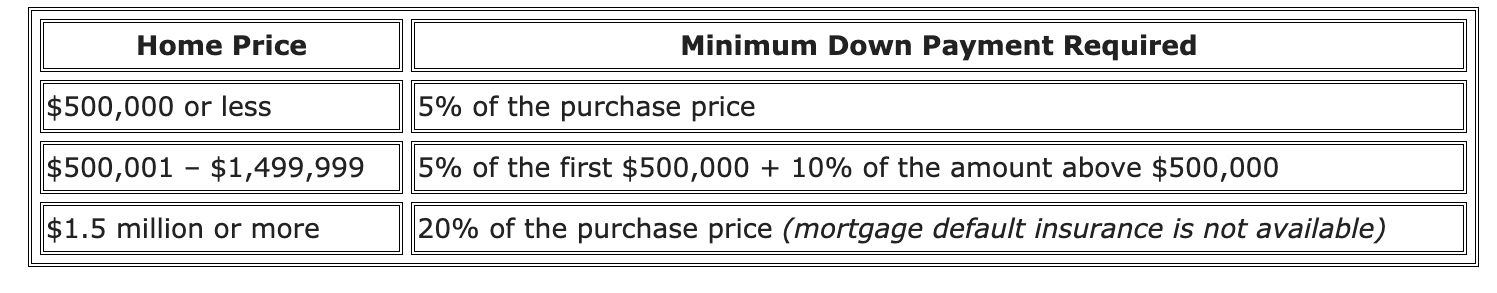
How Much Down Payment Do You Need?
Mortgage Default Insurance Providers
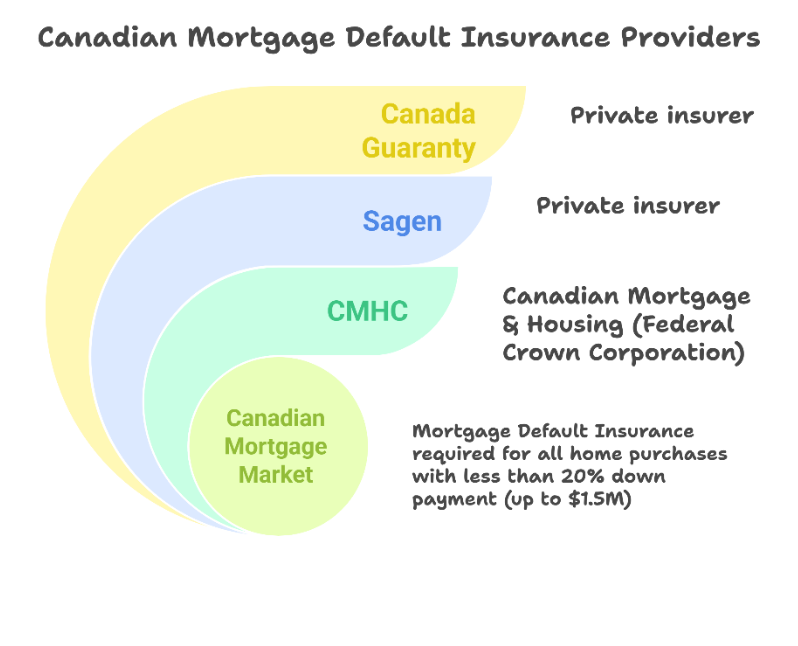
In Canada there are three Mortgage Default Insurance providers:
- Canadian Mortgage & Housing Corp. (CMHC), – a Canadian Federal Crown corporation
- Sagen (formerly Genworth Canada) – a private insurer
- Canada Guaranty – a private insurer
They all have the same rates & sliding scale - the larger your down payment the less insurance you pay, since you are considered less “risky”.
Your lender selects the mortgage insurer, not you. Each insurer assesses borrowers and properties differently. Sometimes, your lender may approve your mortgage, but the insurer might decline it. If all three insurers decline, you won’t get approved for a mortgage with less than 20% down payment.
How Mortgage Default Insurance Premiums Work
The smaller your down payment, the higher the Mortgage Default insurance premium.
- Good news – Insurance Premiums can be rolled into your mortgage amount
- Bad news - this means you’ll pay interest on the insurance premium for the life of your mortgage (usually 25 or 30 years).
- Alternatively, you can pay the premium upfront as part of your closing costs.
Current Mortgage Default Insurance premium rates based on down payment size:
- 5% - 9.99% down payment: 4.00%
- 10% - 14.99% down payment: 3.10%
- 15% - 19.99% down payment: 2.80%
Mortgage Default Insurance in Action
If you stop making mortgage payments, the insurer covers the lender's financial losses. However, this doesn't absolve you of responsibility. If the property sells for less than the outstanding mortgage, you're still personally responsible for any shortfall.
Mortgage Default Insurance Exceptions to Keep in Mind
- Investment properties are not eligible for mortgage insurance; consequently, you will need a minimum 20% down payment to buy.
- The maximum amortization for an insured mortgage is 25 years.
- Dec. 15, 2024 – 30-year amortization available for First Time Home Buyers OR buying a Prebuild
- Using Federal RRSP rules
- Dec. 15, 2024 maximum home price increased to $1.5 million (was $1M)
- Homes over $1.5 million do not qualify for Mortgage Default Insurance.
- Lenders might still require mortgage insurance even if your down payment exceeds 20% based on property type or location.
Why Mortgage Default Insurance Matters
Mortgage insurance benefits home buyers by allowing lenders to offer lower interest rates, despite smaller down payments. Without this insurance, lenders would charge much, much higher interest rates due to increased risk.
- You pay the mortgage default insurance and if something goes horribly wrong in your life regarding your mortgage, the lender can go to the insurance company to recoup their loses.
Ideally, providing a 20% down payment is the best option, but if that's not feasible, Mortgage Default Insurance can make homeownership achievable.
If you default on a mortgage that’s protected by mortgage default insurance, here's what happens:
- Lender Claims Insurance:
Your lender will sell the property to recover the outstanding mortgage balance. If the sale doesn't cover what's owed, the lender files a claim with the mortgage insurer (e.g., CMHC, Sagen, Canada Guaranty). - Insurer Pays the Lender:
The mortgage insurer compensates the lender for the shortfall. - You Remain Liable:
Mortgage Default Insurance does NOT protect you… it protects your mortgage lender. You are still personally responsible for repaying any remaining outstanding balance. The mortgage insurer (or lender) can legally pursue you for this outstanding debt, potentially affecting your credit and financial future.
Mortgage default insurance protects the lender—not you—so it’s critical to understand your ongoing obligations in default scenarios.
Final Thoughts
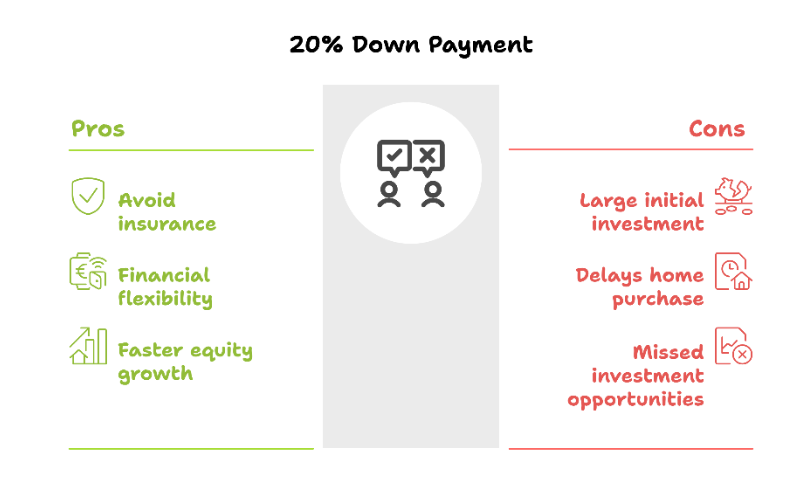
Whenever possible, aim for
at least a 20% down payment. It helps you avoid mortgage default insurance premiums and gives you more financial flexibility.
- Check out my BLOG: 5 GREAT Reasons To Provide a 20% Down Payment when Buying a Home
But if 20% isn’t realistic for you right now, Mortgage Default Insurance can help you move forward confidently—and get into your home sooner.
Need help
navigating your home buying & mortgage financing options? I’d be happy to guide you through what’s possible.







